Camotes Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Camotes Islands is a group of islands in the
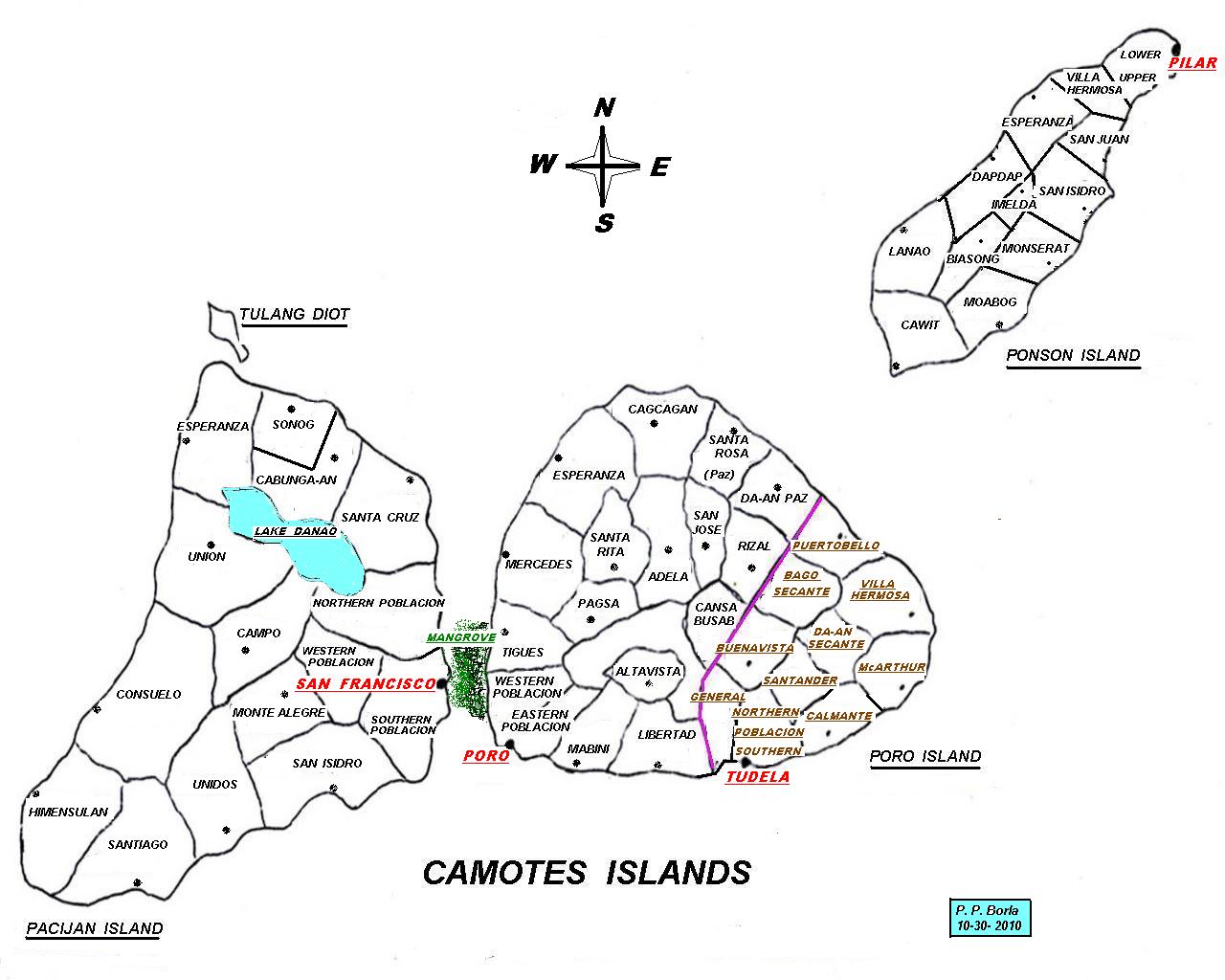 Camotes Islands comprises three major islands and one minor islet, divided between four municipalities. On
Camotes Islands comprises three major islands and one minor islet, divided between four municipalities. On
Mystical Tudela WebsiteHow to get to Camotes IslandCamotes Islands Travel GuideTourCamotes.Com: All About Camotes Islands, Cebu, PhilippinesCebu DestinationsLocal government site
{{Authority control Beaches of the Philippines Islands of Cebu
Camotes Sea
The Camotes Sea is a small sea within the Philippine archipelago, situated between the Central Visayan and the Eastern Visayan regions. It separates Cebu from Leyte hence is bordered by Cebu to the west, Leyte to the east and north, and Bohol ...
, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. Combined area is . The island group is located east of Cebu Island
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 1 ...
, southwest of Leyte Island
Leyte ( ) is an island in the Visayas group of islands in the Philippines. It is eighth-largest and sixth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 2,626,970 as of 2020 census.
Since the accessibility of land has be ...
, and north of Bohol Island
Bohol (), officially the Province of Bohol ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bohol; tl, Lalawigan ng Bohol), is an island province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, consisting of the island itself and 75 minor surrounding islands. It ...
. It is from Cebu City
Cebu City, officially the City of Cebu ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Sugbo; fil, Lungsod ng Cebu; hil, Dakbanwa sang Sugbo), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Central Visayas region of the Philippines and capital of the Cebu Province. Acc ...
and is part of Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 16 ...
. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 102,996. Population has grown % since 1990, equivalent to an annual growth rate of .
Nearest landfall, from north end of Ponson island to southern Leyte, is about . From Consuelo port to Danao is as the crow flies. From south of Pacijan to Bohol is about .
Sometimes known as the "''Lost Horizon'' of the south", within recent years Camotes has seen increased visitors and tourism and a growing expatriate community. Apart from natural attractions on land, there is also a score of dive sites around the islands.
Geography
 Camotes Islands comprises three major islands and one minor islet, divided between four municipalities. On
Camotes Islands comprises three major islands and one minor islet, divided between four municipalities. On Poro Island
Poro Island (Filipino: Pulo ng Poro) is an island in the province of Cebu, located east of Cebu Island and west of Leyte Island. Two municipalities, Poro and Tudela, are located on Poro Island. It is one of the four Camotes Islands along with Pac ...
are the municipalities of Poro
The Poro, or Purrah or Purroh, is a men's secret society in Sierra Leone, Liberia, Guinea, and the Ivory Coast, introduced by the Mane people. It is sometimes referred to as a hunting society and only males are admitted to its ranks. The femal ...
and Tudela. Pacijan Island's sole municipality is San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
. Ponson Island Ponson may refer to:
Places
* Ponson Island, an island located in the province of Cebu
* Carcen-Ponson, a commune in south-western France
* Ponson-Dessus, a commune in south-western France
* Ponson-Debat-Pouts, a commune in south-western France
...
's sole municipality is Pilar. Tulang Island
San Francisco, officially the Municipality of San Francisco ( ceb, Lungsod sa San Francisco; tgl, Bayan ng San Francisco), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Cebu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59 ...
is an islet and part of San Francisco. The main islands of Pacijan and Poro are connected by a causeway. Ponson lies about northeast of Poro, across the Kawit Strait. Tulang is located a short distance north of Pacijan.
The Camotes are low-lying with several hills, some used for telecommunications relay stations. The highest point is Altavista, above sea level, on Poro. Pacijan has a large lake, Lake Danao Lake Danao may refer to lakes in the Philippines:
* Lake Danao (Cebu) in the province of Cebu
* Lake Danao (Leyte) in the province of Leyte
* Lake Danao (Negros) in the province of Negros Oriental
* Lake Danao, also called Cabilao Island Lake, on C ...
, which at is the largest freshwater lake in the province.
Demographics
Languages
Cebuano is the primary language, then English andFilipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
. School children are taught all three languages.
Porohanon or Camotes Visayan is spoken in the town of Poro only, and is one of the most endangered languages in the Visayas. The language is classified as distinct from Sebwano (Bisaya) by the Komisyon ng Wikang Filipino
, logo =
, logo_width =
, logo_caption =
, seal = Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino (KWF).svg
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, formed = 1937 (first formation)1991 (reformed)
, preceding1 ...
and is vital to the culture and arts of the Porohanon people
Poro Island (Filipino: Pulo ng Poro) is an island in the province of Cebu, located east of Cebu Island and west of Leyte Island. Two municipalities, Poro and Tudela, are located on Poro Island. It is one of the four Camotes Islands along with ...
.
The dialect is very similar to the language spoken in the rest of Camotes Islands and throughout the province of Cebu, Northern Mindanao and other parts of the Visayas. Porohanon is distinguished by the way the locals substitute the /y/ sound for /z/. Example: ''maayong buntag'' (good morning) in Cebuano would be changed to ''maazong buntag'' in Porohanon, ''na-a diha'' (in Cebuano), ''ara dira'' (in Porohanon)
Transport
Environment
Climate
Tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
category "Am"), with rainfall more or less evenly distributed throughout the year – Coronas climate type IV.
Biota
By Presidential Proclamation 2152 of 1981, the islands of Ponson, Poro and Pacihan were declared Mangrove swamp forest reserves. Exemplars of the rare, critically endangered tree species Cebu Cinnamon (''Cinnamomum cebuense'') have been discovered on the Camotes Islands.Palm tree
The Arecaceae is a family of perennial flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are called palm ...
s are the dominant plant on the islands. There are also numerous native varieties of fruit including banana, mango and pineapple.
History
Protohistory
Little is known of the islands' early history. The twentieth century saw a number of archaeological studies, but nothing of major significance emerged. An early visitor was Carl Guthe, who led an expedition from the University of Michigan which spent three years 1923–1925 investigating and exploring many sites across the archipelago. He conducted an archaeological dig in a cave site on Tulang. Located on the southeastern coast of the island, the cave measures about . Guthe reported it to contain bone fragments and teeth of about 60 individuals. Associated grave goods included earthenware pottery, shell bracelets, bronze and iron artefacts (iron tang, bronze chisel, iron blade), glass and stone beads, hammerstone and pestle. Filed teeth were also recovered from this site. Otley Beyer (Philippine's "Father of Anthropology") never visited, although he is reported to have described Camotes as a "basket of interesting archaeological finds." In the early 1970s, residents unearthed a variety of artefacts dating back to the 16th century. An excavation at Mactang, a ''purok'' within Esperanza, Poro, revealed spears, daggers, swords, crosses, iron pendants and a skull pierced with an arrowhead. This heavily disturbed and looted site located along the shoreline of sitio Mactang was excavated by Bailen and Cabanilla of UP Diliman in the early 1990s and explored by Bersales and USC in 2001. Porcelain and earthenware sherds are strewn on the surface of what would otherwise have been a 13th- or 14th-century CE burial site. In one barangay, Bailen and Cabanilla found a complex of caves which they believed had been inhabited by primitive people. Cabanilla asked municipal officials to preserve the site and wait while their project proposal would be approved. They planned to conduct a digging and leave whatever artefacts would be found in the caves. Meaning, they would transform the place into an onsite museum that should attract students, archaeologists. etc. A few months later, Cabanilla returned to Camotes, having secured project funding from a foreign institution. To his surprise and dismay, despite earlier assurances of its safekeeping, he found the caves already mined of stone which had been sold to a sinter plant in Leyte by the mayor. Only one cave remained, but Cabanilla lost the drive and returned to Manila, his project scuttled. Because of that, even the plan to set up a town museum for the artifacts dug during the survey was abandoned.Spanish conquistadores
The islands were first mentioned byAntonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was an Venetian scholar and explorer. He joined the expedition to the Spice Islands led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan under the flag of the emperor Charles V and after Magellan's death in the Philippine Islands, ...
, one of the survivors on Ferdinand Magellan's fateful voyage, as they waited off the islands for several days before going on to Cebu in the first week of April 1521:
Writing in 1582, Miguel de Loarca stated:
He also wrote:
:"''todos son de vna manera tienen tambien gallinas y puercos y algunas cabras frisoles y vnas Rayçes como batatas de sancto domingo qe llaman camotes''
:All are provided with fowls, swine, a few goats, beans, and a kind of root resembling the potatoes of Sancto Domingo, called by the natives ''camotes''." This remark is itself remarkable in that "camote" is the Hispanicized form of the Nahuatl (indigenous Mexican) word for " sweet potato", indicating a prior visit by a Spanish ship from Mexico.
Camotes Islands were previously a part of the Leyte province before being transferred to Cebu province during the American period.
Modern times
In 1942 Japanese forces occupied Camotes Islands. In 1945 Japanese soldiers massacred almost all of the inhabitants in Pilar which led to a war crimes trial after the war. The liberation of the islands happened soon after the massacre when Philippine and American soldiers landed and fought the remaining Japanese soldiers in theBattle of Camotes Islands
The Battle of Camotes Islands in the Pacific campaign of World War II was the amphibious invasion of the Poro Island in the Philippines by United States forces, who fought against the Imperial Japanese Army in the Philippines from 17 Octobe ...
.
Economy
The predominant industries on the Camotes Islands are farming (including corn, rice, pigs, chicken and cattle), fishing and tourism. There are about 22 tourist resorts catering to both domestic and international visitors with many public and private beaches. Also in the Camotes Islands you can find tourist spots such as Buho Rock, Greenlake Park, Mt. Calvary (Kalbaryo), Lake Danao and the vast mangrove swamp along the sides of the road from Pacijan (San Francisco) to Poro. There are many caves such as Bukilat Cave, Timubo Cave and Guadalupe Cave which has a fresh-water underground lake. There are also two waterfalls, one in Poro and one in Tudela. There is diving and snorkeling opportunities at some of the resorts. The major employers are CELCO (Camotes Electric Cooperative), Camotes Hillside Academy and Kinoshita Pearl Farm. There is a small hospital. Fiesta Mall, the first mall on the island opened in 2015. A new integrated casino resort with condos is scheduled to open in December, 2016. Tourism in the key economic development for the future of the island with a focus on the white sand beaches, safe and clean environment. There are two colleges on the island: Cebu Technology University (Camotes) and Mount Moriah College.Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Mystical Tudela Website
{{Authority control Beaches of the Philippines Islands of Cebu